Guide to AVR ISP Circuits
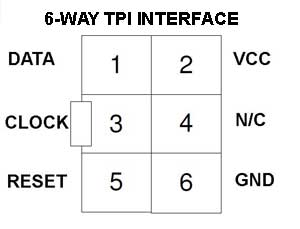
This guide covers Serial Programming, which is commonly called ISP, not JTAG programming which uses a different connector and algorithm. JTAG interface is used for debugging on larger AVR devices (40-pin plus) and can be used for programming as well. Most Kanda AVR programmers also support JTAG. Please see below for AVR JTAG, TPI and UPDI interfaces.In System Programmers have different amounts of "drive" depending on their price and design, so for maximum flexibility in choosing a programmer, err on the side of caution with sizes unless you have compelling reasons for fitting large capacitors and low value resistors.
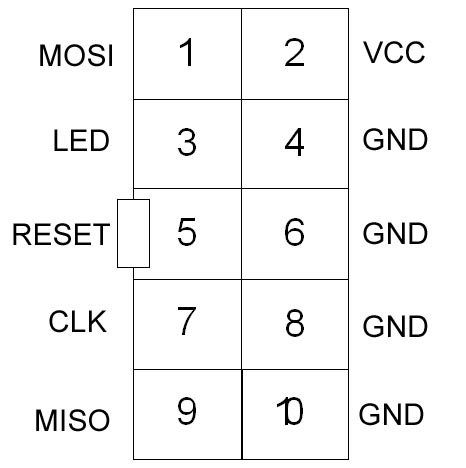
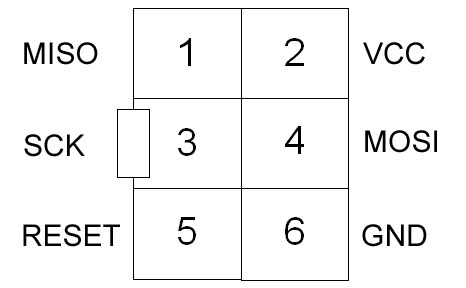
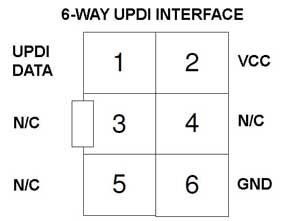
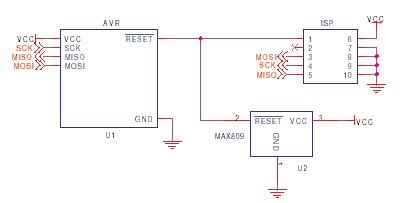
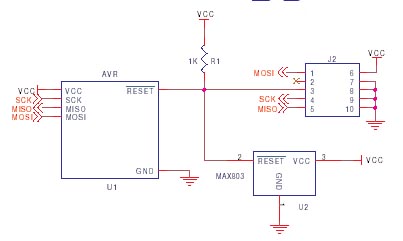
The AVR ISP connector can be either 6 or 10-way, but this makes no difference to your circuit layout. 10-way connectors have more Ground lines to improve noise immunity during programming.
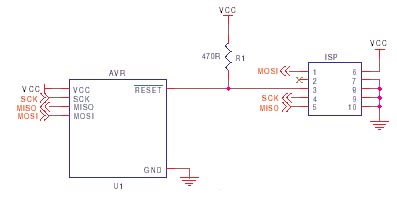
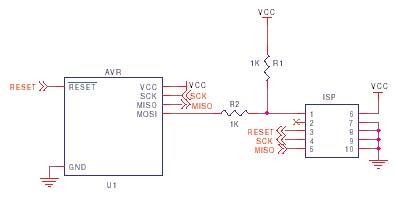
Simple AVR ISP Circuit
The simplest AVR ISP circuit is shown here, with some notes. Ground and VCC must be connected to programmer, either to power programmer, allow programmer to power target or to provide a reference voltage for lower voltage circuits.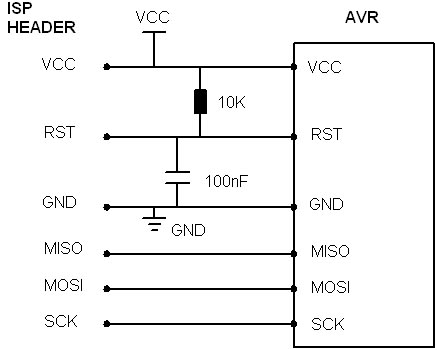
- Most AVR microcontrollers use MOSI, MISO and SCK SPI pins for programming, but some
such as ATmega128 use SPI SCK but use UART TX and RX pins instead for MISO and MOSI. This setup
causes more problems than anything else so beware.
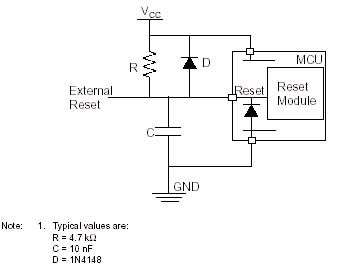
- The capacitor connected between Reset and Ground, and the resistor from Reset to Vcc
should be fitted to give a slight delay to allow AVR to power up properly. These values
are not critical, but if they are too large then the ISP programmer will need to be slowed down.
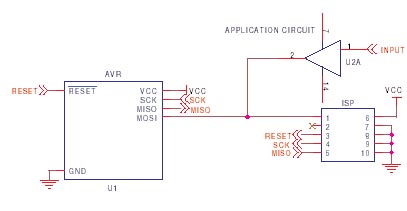
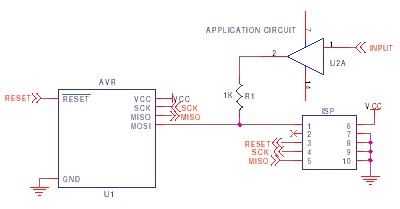
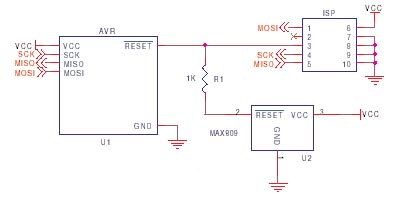
- The programming lines (SCK, MISO and MOSI) are best left just for programming, but if these pins
must be used by the application, then resistors should be used to isolate the application
circuitry, typically 4K7. This is especially important if TXD/RXD are used for programming,
as UART chips tend to hold the lines.
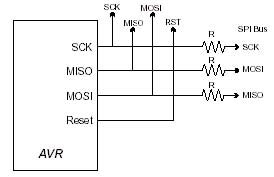
This should be fine for SPI or UART use or where pins are inputs but if you have to use these lines for higher current, then a multiplexer circuit may be needed, see STK200 schematics. - Capacitors on the programming lines can cause problems, especially on SCK. If they have to be fitted,
then they should be below 10nF and fitted as close as possible to AVR microcontroller pins.
Some low cost programmers will have problems with even a 10nF capacitor on SCK or MOSI, so smaller
is better.
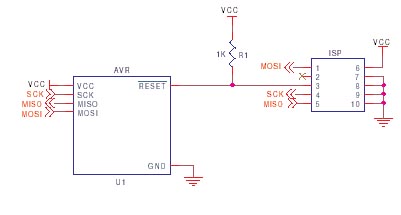
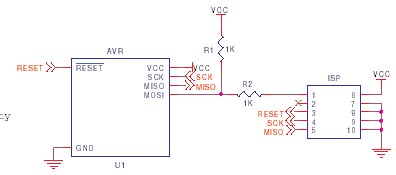
Atmel AVR ISP Reset Circuit
Atmel recommend that a diode is fitted between Reset and Vcc as shown here, but we have not found it necessary in practice. Note their recommended resistor and capacitor values are slightly different, but these values are not critical. A capacitor between 10nF and 100nF and a resistor between 4K7 and 10K will be fine.